Can Glaucoma Kill A Dog? Understanding The Risks, Symptoms, And Treatment
Glaucoma in dogs is a serious condition that can lead to blindness and, in severe cases, even death if left untreated. This condition occurs when there is an abnormal increase in intraocular pressure (IOP) within the eye. When this pressure becomes too high, it can damage the optic nerve and other parts of the eye, leading to permanent vision loss. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for glaucoma is crucial for any dog owner who wants to ensure the long-term health and well-being of their pet.
Glaucoma is not just a vision-related issue; it can also cause immense pain and discomfort for your furry friend. Early detection and timely intervention are key to managing this condition effectively. In this article, we will explore everything you need to know about glaucoma in dogs, including its potential to be life-threatening and how to prevent it from escalating into a fatal condition.
By the end of this article, you will have a comprehensive understanding of how glaucoma affects dogs, the signs to look out for, and the steps you can take to protect your dog from this debilitating condition. Let's dive in!
- St John Bosco Schools
- Curtis Ingraham Net Worth
- The Silver And Gold Is Mine
- Where Is The Legacy Museum
- Kebek 3 Old Orchard Beach Maine
Table of Contents
- What is Glaucoma?
- Types of Glaucoma in Dogs
- Causes of Glaucoma
- Symptoms of Glaucoma
- Diagnosis of Glaucoma
- Treatment Options
- Can Glaucoma Kill a Dog?
- Prevention of Glaucoma
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Conclusion
What is Glaucoma?
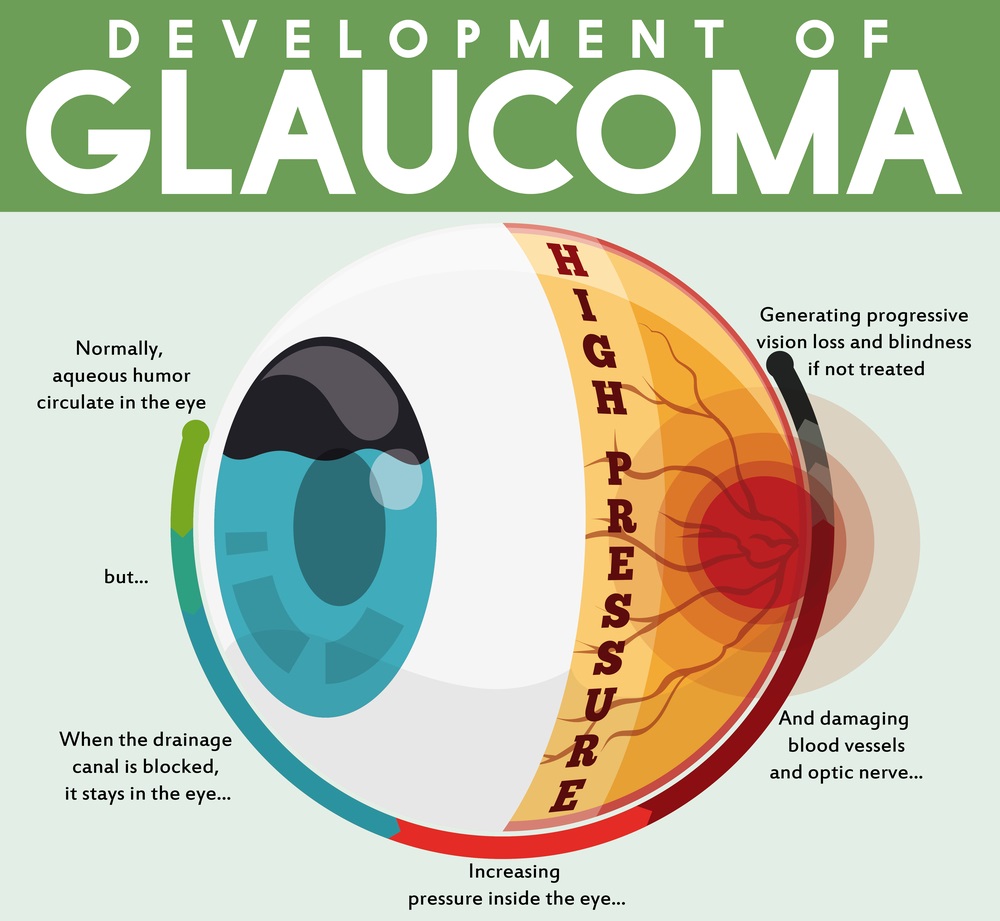
Glaucoma is a medical condition that affects the eyes of both humans and animals, including dogs. It occurs when the fluid inside the eye, known as aqueous humor, does not drain properly, leading to an increase in intraocular pressure (IOP). This elevated pressure can cause damage to the optic nerve, which is responsible for transmitting visual information from the eye to the brain.
In dogs, glaucoma is often painful and can lead to irreversible blindness if not addressed promptly. The condition can develop in one or both eyes and may vary in severity depending on the underlying cause and how quickly it is diagnosed and treated.
Types of Glaucoma in Dogs
There are two primary types of glaucoma in dogs: primary and secondary glaucoma.
- Shoe Stores At University Park Mall
- Kob%C3%83 Japanese Steakhouse West 192
- Family Care Eye Center
- Earls Funeral Home Barbados
- Indiana Beach Amusement And Water Park
Primary Glaucoma
Primary glaucoma is an inherited condition that occurs due to genetic predisposition. Certain breeds, such as Cocker Spaniels, Basset Hounds, and Beagles, are more prone to developing this type of glaucoma. It typically affects both eyes, although one eye may be affected first.
Secondary Glaucoma
Secondary glaucoma is caused by another underlying condition or injury that disrupts the normal drainage of aqueous humor. Common causes include inflammation, trauma, tumors, and lens dislocation. This type of glaucoma can occur in any breed and may affect only one eye initially.
Causes of Glaucoma
The exact cause of glaucoma depends on the type. Primary glaucoma is primarily genetic, while secondary glaucoma can result from a variety of factors. Some of the most common causes include:
- Inflammation of the eye (uveitis)
- Trauma or injury to the eye
- Tumors or cancer in or around the eye
- Luxation or displacement of the lens
- Blockage of the drainage angle
Understanding the specific cause of glaucoma in your dog is essential for determining the appropriate treatment plan.
Symptoms of Glaucoma
Recognizing the symptoms of glaucoma early is critical for preventing permanent damage. Some of the most common signs include:
- Persistent redness in the eye
- Cloudy or bluish appearance of the cornea
- Squinting or excessive blinking
- Swelling or bulging of the eye
- Loss of vision or blindness
- Behavioral changes, such as increased irritability or lethargy
If you notice any of these symptoms in your dog, it is important to seek veterinary care immediately. Delaying treatment can result in irreversible damage to the eye and increased pain for your pet.
Diagnosis of Glaucoma
Diagnosing glaucoma in dogs involves a thorough examination by a veterinarian or veterinary ophthalmologist. The following diagnostic tools and techniques may be used:
- Tonometry: A device called a tonometer is used to measure the intraocular pressure (IOP) in the eye.
- Ophthalmoscopy: This allows the veterinarian to examine the structures inside the eye, including the retina and optic nerve.
- Gonioscopy: This technique is used to evaluate the drainage angle of the eye and determine whether it is open or closed.
- Ultrasound: In cases where the eye is too cloudy to see through, an ultrasound may be used to assess the structures within the eye.
Early diagnosis is crucial for effective treatment and management of glaucoma in dogs.
Treatment Options
Treatment for glaucoma in dogs aims to reduce intraocular pressure, alleviate pain, and preserve vision when possible. The specific treatment plan will depend on the type and severity of glaucoma, as well as the underlying cause.
Medical Treatment
Medical treatments for glaucoma often involve the use of topical or systemic medications to lower IOP. Some common medications include:
- Prostaglandin analogs: These drugs increase the outflow of aqueous humor from the eye.
- Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors: These medications reduce the production of aqueous humor.
- Osmotic agents: These are used to temporarily reduce IOP in emergency situations.
Surgical Options
In cases where medical treatment is insufficient, surgical intervention may be necessary. Some common surgical procedures include:
- Goniosurgery: This involves creating a new drainage pathway for aqueous humor.
- Ciliary body ablation: This procedure reduces the production of aqueous humor by destroying part of the ciliary body.
- Enucleation: In severe cases where the eye is beyond saving, surgical removal of the eye may be necessary to relieve pain.
Can Glaucoma Kill a Dog?
While glaucoma itself does not directly cause death, the complications associated with untreated glaucoma can be life-threatening. The extreme pain and discomfort caused by high intraocular pressure can lead to behavioral changes, decreased appetite, and overall poor quality of life. In some cases, untreated glaucoma can lead to secondary infections or systemic issues that may compromise the dog's health.
Moreover, if a dog is suffering from severe pain due to glaucoma, euthanasia may be considered as a humane option to prevent further suffering. Early intervention and proper management of glaucoma are essential to avoid these outcomes and ensure your dog's well-being.
Prevention of Glaucoma
While primary glaucoma cannot be prevented due to its genetic nature, there are steps you can take to reduce the risk of secondary glaucoma and manage the condition in predisposed breeds:
- Regular eye examinations: Schedule routine check-ups with a veterinarian, especially if your dog is a breed prone to glaucoma.
- Protect your dog's eyes: Avoid situations where your dog's eyes may be injured, such as rough play or exposure to harmful chemicals.
- Monitor for early signs: Be vigilant for any changes in your dog's eyes or behavior that may indicate glaucoma.
- Genetic testing: Consider genetic testing for breeds known to be at risk for primary glaucoma.
By taking proactive steps, you can help ensure your dog's eyes remain healthy and reduce the risk of developing glaucoma.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are some common questions about glaucoma in dogs:
1. Is glaucoma in dogs painful?
Yes, glaucoma can be extremely painful for dogs due to the high intraocular pressure. It is important to address the condition promptly to alleviate discomfort.
2. Can glaucoma in dogs be cured?
While glaucoma cannot be cured, it can be managed with proper treatment to preserve vision and relieve pain.
3. How long can a dog live with glaucoma?
The lifespan of a dog with glaucoma depends on the severity of the condition and how effectively it is managed. With appropriate treatment, many dogs can live comfortably for years despite having glaucoma.
Conclusion
Glaucoma is a serious condition that can have devastating effects on a dog's vision and overall health. Understanding the risks, symptoms, and treatment options is essential for any dog owner. While glaucoma itself may not directly kill a dog, the complications associated with untreated glaucoma can significantly impact their quality of life and, in severe cases, lead to euthanasia.
By staying informed and proactive, you can help protect your dog from the harmful effects of glaucoma. Regular veterinary check-ups, early detection, and prompt treatment are key to managing this condition effectively. If you suspect your dog may have glaucoma, don't hesitate to seek professional veterinary care.
We encourage you to share this article with other dog owners and leave your thoughts or questions in the comments below. Together, we can raise awareness about glaucoma in dogs and ensure our furry friends live long, healthy lives!
- Animal Hospital In Crystal Lake Il
- What Age Do Kittens Drink Water
- Andretti Karting Atlanta Ga
- Indiana Beach Amusement And Water Park
- Doubletree Hotel International Drive Orlando Fl

Gordon's® Brush Killer For HardtoKill Brush
Awareness Screen, Protect & Cure Dr. John D. Bissell O.D.

Baldur's Gate 3 loophole lets you complete Wyll's quest to kill Karlach