What Country Is On The Horn Of Africa? Exploring The Geopolitical And Cultural Hub
The Horn of Africa is one of the most significant regions in the world, both geographically and geopolitically. Located in the easternmost part of the African continent, it plays a crucial role in global trade, migration, and cultural exchange. Understanding what country is on the Horn of Africa is essential for anyone interested in geography, history, and international relations.
The Horn of Africa has long been a focal point of global attention due to its strategic location near the Red Sea and the Gulf of Aden. It serves as a bridge between Africa and Asia, making it a critical area for trade routes and maritime navigation. This region is not only rich in history but also a melting pot of cultures and ethnicities.
In this article, we will explore the countries that make up the Horn of Africa, their unique characteristics, and their geopolitical significance. By the end of this article, you will have a comprehensive understanding of what country is on the Horn of Africa and why it matters.
- Universal Studios Hollywood Whoville
- Why Is Cvs Charging Me 5 A Month
- Leaf And Bud Photos
- El Jefe Taqueria Boston
- What Cancer Did Gabe Solis Died From
Table of Contents
- Geography of the Horn of Africa
- Countries on the Horn of Africa
- Ethiopia: The Heart of the Horn
- Somalia: A Nation of Resilience
- Eritrea: A Land of Diversity
- Djibouti: The Gateway to Africa
- Historical Significance of the Horn
- Economic Importance of the Region
- Challenges Facing the Region
- The Future of the Horn of Africa
Geography of the Horn of Africa
The Horn of Africa is a peninsula in the northeastern part of the African continent. It protrudes into the Arabian Sea and lies along the southern side of the Red Sea. This region is characterized by its diverse landscapes, ranging from arid deserts to fertile highlands. The geography of the Horn plays a pivotal role in shaping its culture, economy, and geopolitical dynamics.
Key geographical features of the Horn of Africa include the Ethiopian Highlands, the Ogaden Desert, and the Gulf of Aden. The region's strategic location near the Bab-el-Mandeb Strait makes it a vital chokepoint for global maritime trade. Understanding the geography of the Horn is crucial to comprehending the region's significance in world affairs.
Why is the Horn of Africa Strategically Important?
The strategic importance of the Horn of Africa cannot be overstated. It serves as a gateway between the Indian Ocean and the Mediterranean Sea, making it a critical area for international trade. Additionally, the region's proximity to the Middle East and Europe has made it a focal point for geopolitical tensions and alliances.
- Hotel The Hague Marriott
- La Copa South Padre Island Reviews
- Scott Peterson New Theory
- Walmart Hagerstown Md Sharpsburg Pike
- Pymatuning State Park Spillway
Countries on the Horn of Africa
Four countries make up the Horn of Africa: Ethiopia, Somalia, Eritrea, and Djibouti. Each of these nations has its own unique characteristics and contributes to the region's rich tapestry of culture and history. In the following sections, we will explore each country in detail.
Ethiopia: The Heart of the Horn
Ethiopia is the largest and most populous country on the Horn of Africa. Known for its ancient history and rich cultural heritage, Ethiopia is often referred to as the "Cradle of Humanity" due to the discovery of the oldest known human fossils in the region. The country is home to diverse ethnic groups and languages, with Amharic being the official language.
Ethiopia's Contribution to the Region
- Ethiopia is a founding member of the United Nations and the African Union.
- The country plays a significant role in regional peacekeeping efforts.
- Ethiopia's economy is one of the fastest-growing in Africa, driven by agriculture and manufacturing.
Somalia: A Nation of Resilience
Somalia is another key player on the Horn of Africa. Despite facing decades of civil war and political instability, Somalia has shown remarkable resilience in recent years. The country is known for its vibrant culture, including poetry, music, and art. Somalia's coastline along the Indian Ocean makes it an important player in regional maritime trade.
Somalia's Economic Potential
- Somalia has vast untapped natural resources, including oil, gas, and minerals.
- The country's fishing industry is a significant contributor to its economy.
- Remittances from the Somali diaspora play a crucial role in supporting the local economy.
Eritrea: A Land of Diversity
Eritrea, located along the Red Sea coast, is a country of diverse cultures and landscapes. The country gained independence from Ethiopia in 1993 after a long and protracted war. Eritrea's strategic location makes it an important player in regional geopolitics. The country is home to several ethnic groups, including the Tigrinya, Tigre, and Afar.
Eritrea's Strategic Location
Eritrea's coastline along the Red Sea gives it access to one of the busiest shipping lanes in the world. This strategic advantage has made the country an attractive partner for international powers seeking a foothold in the region. However, Eritrea's political isolation and authoritarian governance have limited its potential to fully capitalize on its strategic assets.
Djibouti: The Gateway to Africa
Djibouti, the smallest country on the Horn of Africa, plays a disproportionately large role in regional and global affairs. Its location at the entrance of the Red Sea makes it a critical hub for international trade and military operations. Djibouti hosts military bases for several countries, including the United States, France, and China, underscoring its strategic importance.
Djibouti's Role in Global Trade
- Djibouti's port is a vital transit point for goods moving between Europe, Asia, and Africa.
- The country's strategic location has made it a hub for logistics and shipping companies.
- Djibouti's partnership with international powers has helped boost its economy and infrastructure development.
Historical Significance of the Horn
The Horn of Africa has a rich and complex history that spans thousands of years. From the ancient Kingdom of Aksum to the rise of Islam and the colonial era, the region has been shaped by a multitude of influences. Understanding the historical context of the Horn is essential to grasping its current geopolitical dynamics.
Key Historical Events in the Horn
- The Kingdom of Aksum, one of the most powerful civilizations in ancient Africa, flourished in the region from the 1st to the 8th century AD.
- The spread of Islam in the 7th century brought significant cultural and religious changes to the Horn.
- The colonial period in the late 19th and early 20th centuries left a lasting impact on the region's political and social structures.
Economic Importance of the Region
The Horn of Africa is a region of immense economic potential. Its strategic location, natural resources, and growing populations make it an attractive destination for investors and businesses. However, the region faces numerous challenges, including poverty, unemployment, and political instability, which hinder its economic development.
Key Economic Sectors in the Horn
- Agriculture remains the backbone of the region's economy, employing a significant portion of the population.
- The service sector, particularly in Ethiopia and Djibouti, is growing rapidly, driven by urbanization and technological advancements.
- The extractive industries, including mining and oil exploration, hold significant promise for the region's future economic growth.
Challenges Facing the Region
Despite its potential, the Horn of Africa faces numerous challenges that threaten its stability and development. Issues such as political instability, terrorism, and climate change pose significant risks to the region's progress. Addressing these challenges requires a coordinated effort from both local and international stakeholders.
Key Challenges in the Horn
- Political instability, including conflicts and governance issues, continues to plague the region.
- Terrorism, particularly from groups like Al-Shabaab, poses a significant threat to regional security.
- Climate change has exacerbated food insecurity and water scarcity in the region, impacting millions of people.
The Future of the Horn of Africa
The future of the Horn of Africa is shaped by both opportunities and challenges. As the region continues to grow and develop, it has the potential to become a major player in global affairs. However, addressing the pressing issues facing the region will require sustained effort and collaboration from all stakeholders.
Opportunities for Growth in the Horn
- Investment in infrastructure, particularly in transportation and energy, can unlock the region's economic potential.
- Regional cooperation and integration can help address common challenges and promote shared prosperity.
- Technological advancements and innovation can drive growth and improve living standards in the region.
Kesimpulan
In conclusion, the Horn of Africa is a region of immense significance, both geographically and geopolitically. Understanding what country is on the Horn of Africa and their unique characteristics is essential for anyone interested in global affairs. From Ethiopia's ancient history to Djibouti's strategic importance, each country in the region plays a crucial role in shaping its future.
We encourage readers to engage with this content by leaving comments or sharing their thoughts on social media. For those interested in learning more about the Horn of Africa, we invite you to explore other articles on our website. Together, we can deepen our understanding of this fascinating region and its role in the world.
- Hy Vee Online Orders
- Grant Holloway And Chase
- La Copa South Padre Island Reviews
- Where Is The Legacy Museum
- Bj S Restaurant In Carlsbad
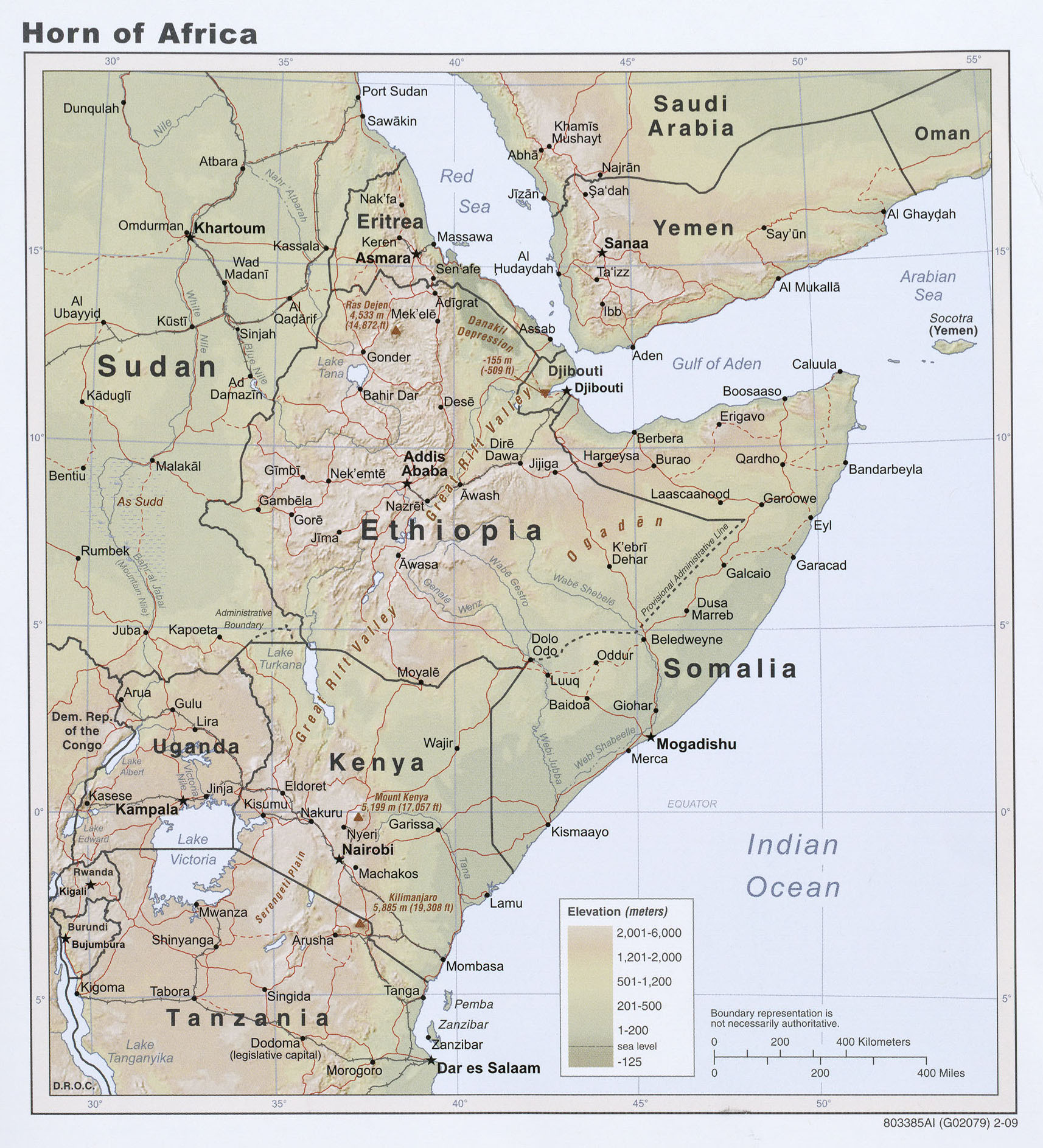
2009 Horn of Africa Physical Relief Map Understanding Horn of Africa
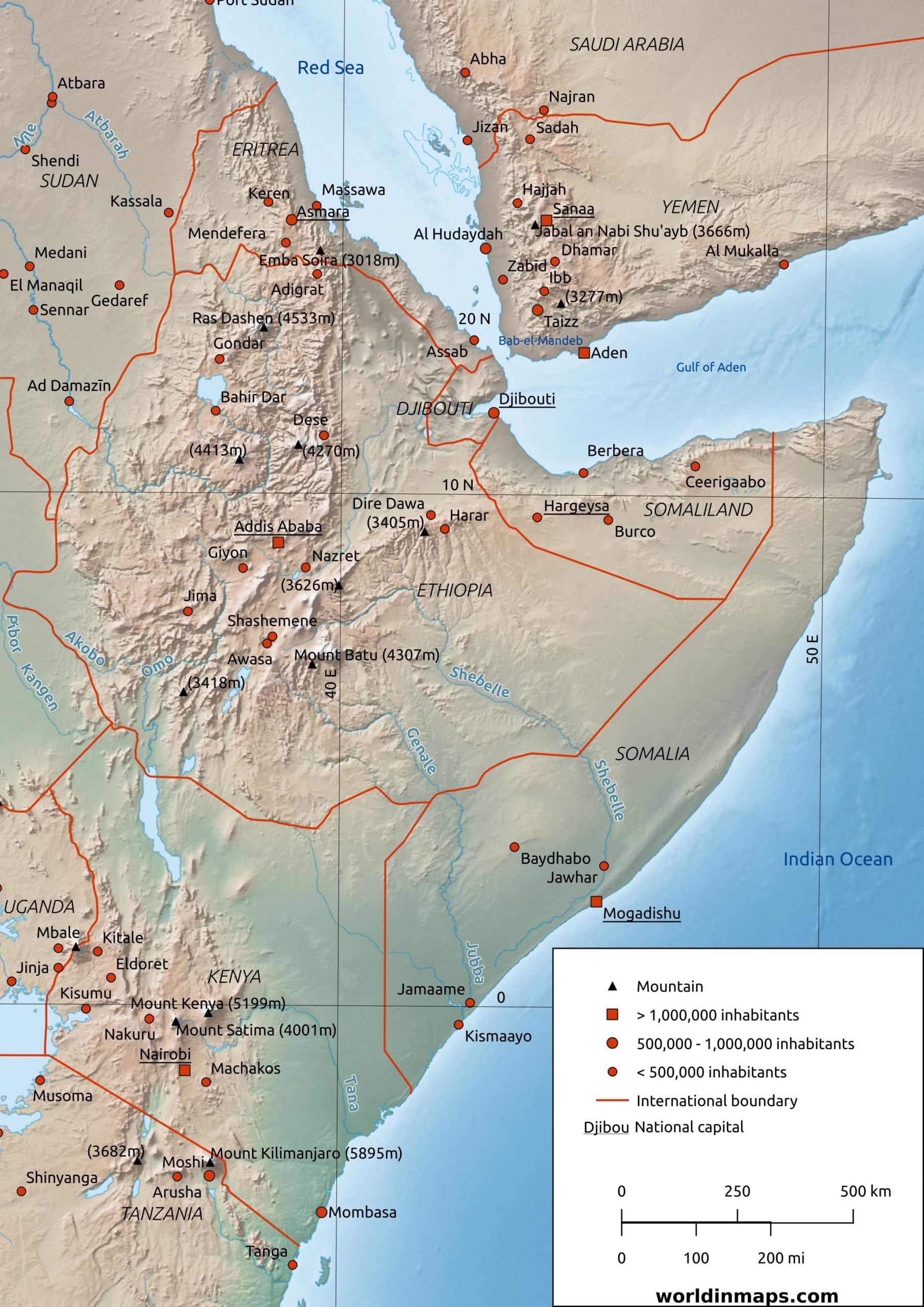
Horn of Africa World in maps

Ethiopia Map Country in the Horn of Africa Stock Vector