Difference Between Sexual Orientation And Gender Identity: A Comprehensive Guide
Understanding the difference between sexual orientation and gender identity is essential in fostering inclusivity and respect in our diverse world. These two concepts, though often conflated, are distinct and have unique meanings. By exploring them in depth, we can gain a clearer understanding of how they shape individual experiences and identities.
Sexual orientation and gender identity are terms frequently discussed in conversations about diversity and human rights. However, many people still struggle to distinguish between the two. This confusion can lead to misunderstandings and even discrimination. In this article, we will delve into these concepts, breaking them down into their core components to provide clarity and insight.
Our goal is to equip you with the knowledge necessary to appreciate the nuances of sexual orientation and gender identity. By doing so, you will be better prepared to engage in respectful dialogues and contribute positively to a more inclusive society.
- The Sebastian Vail Village
- Amc Theaters Near Chicago Il
- What Age Do Kittens Drink Water
- Where Is The Legacy Museum
- What Is King Harris Real Name
Table of Contents
- What is Sexual Orientation?
- Understanding Gender Identity
- Key Differences Between Sexual Orientation and Gender Identity
- Common Misconceptions
- The Importance of Language and Terminology
- The Role of Society and Culture
- Legal and Social Implications
- Supporting LGBTQ+ Communities
- Resources for Further Learning
- Conclusion: Taking Action for Inclusivity
What is Sexual Orientation?
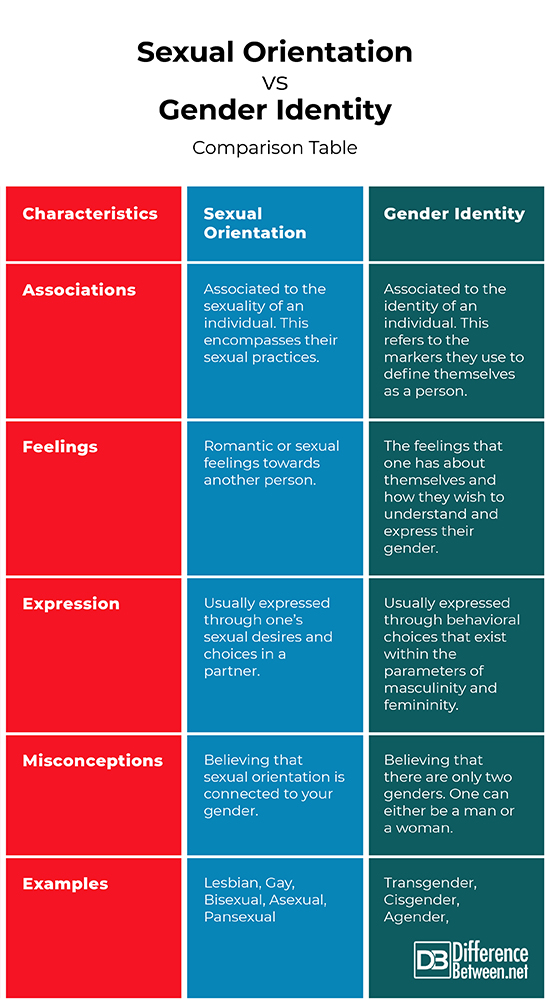
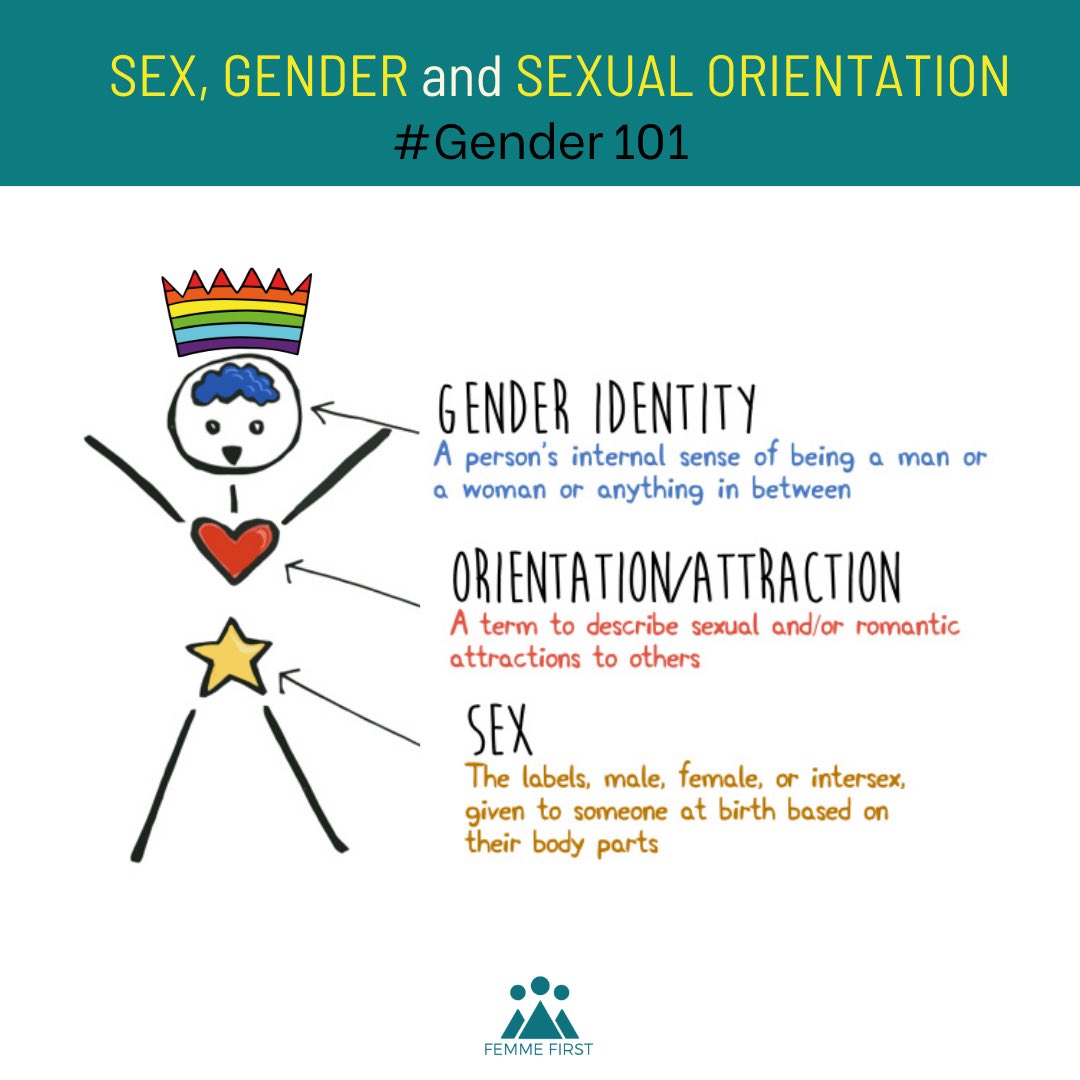
Sexual orientation refers to a person's enduring physical, romantic, and/or emotional attraction to others. It is an inherent aspect of one's identity and is not something that can be changed through external influence or intervention. Common sexual orientations include heterosexual, homosexual, bisexual, pansexual, and asexual, among others.
Research from the Human Rights Campaign highlights that sexual orientation is a spectrum, meaning that people may experience attractions in varying degrees and combinations. Understanding this concept is crucial in recognizing the diversity of human experiences.
It is important to note that sexual orientation is not tied to gender identity. For example, a transgender man who is attracted to men may identify as gay, while a transgender woman who is attracted to women may identify as lesbian. This distinction underscores the need to approach these topics with sensitivity and awareness.
- The Landing At Tiffany Springs
- Heritage Mental Health Clinic
- Leaf And Bud Photos
- Where To Get A Husky Dog
- Dupage Dodge Jeep Chrysler Ram
Types of Sexual Orientation
- Heterosexual: Attraction to the opposite gender
- Homosexual: Attraction to the same gender
- Bisexual: Attraction to both men and women
- Pansexual: Attraction to people regardless of gender
- Asexual: Little to no sexual attraction to others
Understanding Gender Identity
Gender identity is a deeply personal sense of one's own gender. It may or may not align with the sex assigned at birth and is entirely distinct from sexual orientation. Gender identity is an intrinsic part of who someone is and can include identities such as male, female, non-binary, genderqueer, and genderfluid.
The World Health Organization (WHO) recognizes gender identity as a fundamental aspect of human rights. According to WHO, "Gender identity refers to a person's internal and individual experience of gender." This definition emphasizes the importance of respecting each individual's self-identified gender.
For many people, their gender identity aligns with the sex they were assigned at birth. However, for others, this is not the case. Those whose gender identity differs from their assigned sex at birth may identify as transgender or gender non-conforming.
Key Aspects of Gender Identity
- Cisgender: Gender identity aligns with assigned sex at birth
- Transgender: Gender identity differs from assigned sex at birth
- Non-binary: Gender identity exists outside the male/female binary
- Genderfluid: Gender identity shifts or changes over time
Key Differences Between Sexual Orientation and Gender Identity
The difference between sexual orientation and gender identity lies in their definitions and how they manifest in a person's life. Sexual orientation pertains to whom someone is attracted to, while gender identity relates to how someone perceives themselves in terms of gender.
Here are some key distinctions:
- Sexual orientation is about attraction, while gender identity is about self-perception.
- Sexual orientation does not determine gender identity, nor does gender identity determine sexual orientation.
- Both are integral components of a person's identity but operate independently of one another.
Understanding these differences is vital for creating environments that are respectful and inclusive of all individuals, regardless of their sexual orientation or gender identity.
Common Misconceptions
There are several misconceptions surrounding sexual orientation and gender identity that can perpetuate harmful stereotypes. One of the most prevalent myths is that sexual orientation and gender identity are the same thing. This misunderstanding can lead to confusion and even discrimination.
Another misconception is that sexual orientation and gender identity are choices. In reality, both are innate aspects of a person's identity that cannot be altered by external factors. The American Psychological Association (APA) affirms that sexual orientation is not a choice and that efforts to change it, such as conversion therapy, are harmful and ineffective.
Dispelling Myths
- Sexual orientation and gender identity are not interchangeable terms.
- Neither sexual orientation nor gender identity is a choice.
- Conversion therapy is both unethical and harmful.
The Importance of Language and Terminology
Language plays a critical role in shaping our understanding of sexual orientation and gender identity. Using inclusive and respectful language helps create safe spaces for individuals to express themselves authentically. It is important to use the correct pronouns and terminology when referring to someone's gender identity or sexual orientation.
For example, if someone identifies as non-binary, it is respectful to use gender-neutral pronouns such as "they/them." Similarly, it is important to avoid outdated or derogatory terms that may be offensive or hurtful.
Organizations like GLAAD provide valuable resources for learning about appropriate language and terminology. By staying informed and educated, we can contribute to a more inclusive and understanding society.
Respectful Language Tips
- Ask individuals which pronouns they prefer and use them consistently.
- Avoid assumptions about someone's gender identity or sexual orientation.
- Stay updated on evolving terminology and best practices.
The Role of Society and Culture
Society and culture significantly influence perceptions of sexual orientation and gender identity. In many parts of the world, traditional norms and cultural expectations can create barriers for individuals who do not conform to binary gender roles or heterosexual norms. However, progress is being made as more people advocate for LGBTQ+ rights and visibility.
Media representation plays a crucial role in shaping public perceptions. Positive and accurate portrayals of diverse sexual orientations and gender identities help challenge stereotypes and promote acceptance. For example, shows like "Pose" and "RuPaul's Drag Race" have contributed to greater visibility and understanding of transgender and non-binary communities.
Education and awareness campaigns are also essential in fostering inclusivity. By teaching children and adults about the importance of respecting differences, we can create a more compassionate and equitable world.
Cultural Progress and Challenges
- Increased visibility of LGBTQ+ individuals in media and public life.
- Ongoing challenges in regions with restrictive laws and cultural norms.
- Importance of advocacy and education in driving societal change.
Legal and Social Implications
Legal protections and social acceptance are critical for ensuring the well-being of individuals with diverse sexual orientations and gender identities. In many countries, laws have been enacted to protect LGBTQ+ rights, including anti-discrimination laws and recognition of same-sex marriage. However, there is still much work to be done in achieving full equality.
Social attitudes also play a significant role in shaping the experiences of LGBTQ+ individuals. While acceptance has grown in many areas, stigma and discrimination remain prevalent in others. It is important for allies and advocates to continue pushing for change and supporting marginalized communities.
Organizations like the International Lesbian, Gay, Bisexual, Trans and Intersex Association (ILGA) work tirelessly to promote LGBTQ+ rights globally. Their efforts include lobbying for policy changes, providing resources for activists, and raising awareness about human rights violations.
Advancing Legal Protections
- Enactment of anti-discrimination laws in various countries.
- Recognition of same-sex marriage in many regions.
- Ongoing challenges in countries with restrictive laws.
Supporting LGBTQ+ Communities
There are many ways to support LGBTQ+ communities and promote inclusivity. One of the most important steps is to educate oneself about the issues facing these communities and to listen to their voices. Allies can also take action by advocating for policy changes, volunteering with LGBTQ+ organizations, and supporting businesses that prioritize inclusivity.
Creating safe spaces for LGBTQ+ individuals is another crucial step. This can involve establishing gender-neutral restrooms, hosting inclusive events, and ensuring that all members of a community feel welcome and respected.
Finally, it is important to celebrate the diversity and resilience of LGBTQ+ communities. Pride events and other celebrations provide opportunities to honor the progress that has been made while acknowledging the work that still needs to be done.
Ways to Support LGBTQ+ Communities
- Educate yourself about LGBTQ+ issues and history.
- Advocate for policy changes and social justice.
- Volunteer with or donate to LGBTQ+ organizations.
Resources for Further Learning
For those interested in learning more about sexual orientation and gender identity, there are many resources available. Books, articles, and online courses can provide valuable insights into these topics. Additionally, organizations like PFLAG, GLAAD, and the Trevor Project offer support and resources for individuals and families.
Here are some recommended resources:
- Human Rights Campaign: Advocacy and education on LGBTQ+ issues.
- GLAAD: Media advocacy for LGBTQ+ representation.
- The Trevor Project: Crisis intervention and support for LGBTQ+ youth.
Conclusion: Taking Action for Inclusivity
In conclusion, understanding the difference between sexual orientation and gender identity is essential for fostering a more inclusive and respectful society. By recognizing the unique aspects of each concept and appreciating the diversity of human experiences, we can contribute to positive change.
We encourage readers to take action by educating themselves, supporting LGBTQ+ communities, and advocating for equality. Leave a comment below to share your thoughts or questions, and consider sharing this article with others who may benefit from its insights. Together, we can create a world where everyone feels valued and respected.
- How To Install Outside Water Spigot
- Darlings Auto Bangor Maine
- Family Care Eye Center
- Rehoboth Beach Delaware County
- Why Did Dr Phil Lose His License To Practice Psychology
Differences Between Sexual Orientation and Gender Identity Difference
Sexual Orientation? Gender Identity? What's The Difference?, 40 OFF

What is the Difference Between Sexual Orientation and Gender Identity